Valve performance testing
Check content: whether the appearance of the valve has defects, such as cracks, bubbles, dents, etc. Check signage, nameplate and finish for compliance.
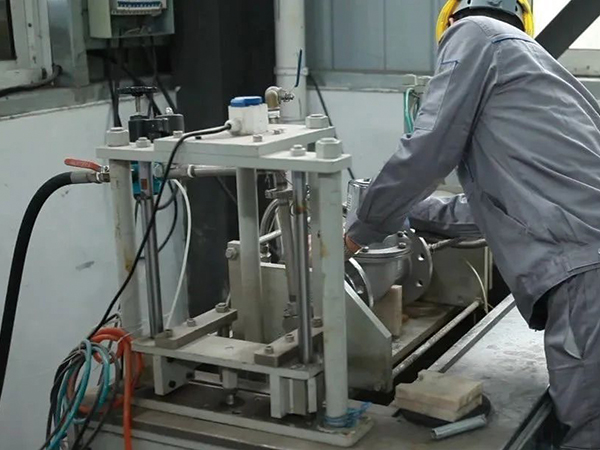

1. Inspection of appearance and logo
Check content: whether the appearance of the valve has defects, such as cracks, bubbles, dents, etc. Check signage, nameplate and finish for compliance.
Standards: International standards including API 598, ASME B16.34, ISO 5208, etc. Chinese standards include GB/T 12224 (general requirements for steel valves), GB/T 12237 (steel ball valves for petroleum, petrochemical and related industries) and so on. Detection method: Through visual inspection and hand inspection, determine whether there are obvious defects on the valve surface, and check whether the identification and nameplate information is correct.
2. Size measurement check content:
Measure key dimensions of valves, including connection ports, body length, stem diameter, etc., to ensure compliance with design drawings and standards.
Standards: International standards include ASME B16.10, ASME B16.5, ISO 5752, etc. China's standards include GB/T 12221 (valve structure length), GB/T 9112 (flange connection size) and so on. Detection method: Use calipers, micrometers and other measuring tools to measure the key dimensions of the valve to ensure that it meets the design requirements.
3. Seal performance test Static pressure test:
Apply static water pressure or static air pressure to the valve, maintain a certain period of time to check the leakage. Low pressure air tightness test: With the valve closed, apply low pressure gas to the inside of the valve and check for leakage. Shell strength test: Apply a hydrostatic pressure higher than the working pressure to the valve to test its shell strength and pressure resistance. Stem strength test: Assess whether the torque or tensile force that the stem is subjected to during operation is within a safe range.
4. Operating performance test Opening and closing torque and speed test:
Test the valve opening and closing torque, opening and closing speed and operating feel to ensure smooth operation and within a reasonable torque range. Flow characteristics test: Test the flow characteristics of the valve at different openings to assess its ability to adjust the fluid.
5. Corrosion resistance test evaluation content:
Evaluate the corrosion resistance of valve materials to working media. Standards: International standards include ISO 9227 (salt spray test), ASTM G85, etc.
Testing method: The valve is placed in the salt spray test chamber to simulate the corrosion environment and test the durability of the material under corrosion conditions.
6. Durability and reliability test Repeated open and close cycle test:
The valve is repeatedly opened and closed to assess its durability and reliability in long-term use. Temperature stability test: Test the performance stability of the valve under different temperature conditions to ensure that it works normally in extreme temperature environments.
Vibration and shock test: the valve is placed on the shaking table or shock table to simulate the vibration and shock in the working environment to test the stability and reliability of the valve.
7. Leak detection Internal leak detection:
Test the internal sealing performance of the valve in the closed state. External leak detection: Check the external tightness of the valve in use to ensure that there is no media leakage.
8. Other tests Safety valve tests:
For the safety valve, it is also necessary to conduct setting pressure and return pressure tests to ensure that it complies with the instructions and relevant regulations.